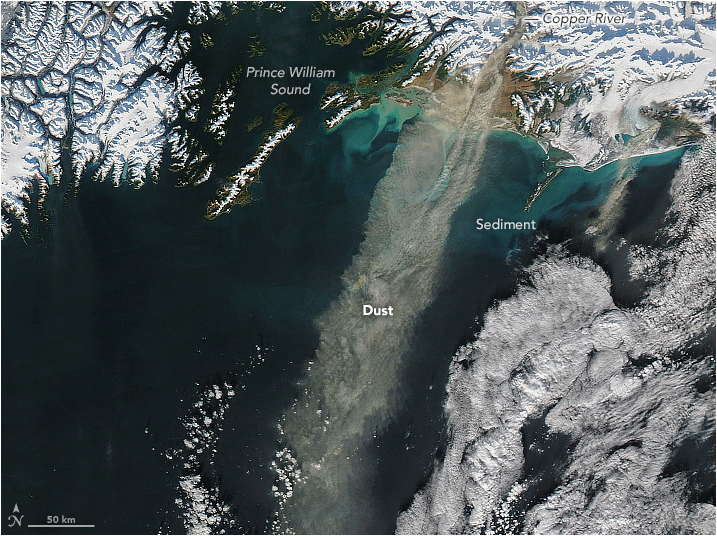
NASA’s Aqua satellite has captured the image of coast along the Gulf of Alaska. On 11th November 2017, NASA’s moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer captured the image of thick plumes of the dust formed as fine-grained loess. The glacial ice shreds rock and the dust storms in the southern Alaska which generally occur in late fall. Although it’s not clear yet that why the increased dust and low levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide would go hand-in-hand. Perhaps, scientists think that dust-triggered in Alaska can absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide.
However, scientists have firstly reported the major dust storms in 1911 in the southern Alaska. And only during the past decades they have begun to find high-latitude dust storms that play a key role in fueling phytoplankton blooms. Later on, in 2011, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center of Santiago Gassó, John of the U.S. Geological Survey along with other scientists published the first study to describe how dust storms play a role in supplying nutrients, especially iron, to the Gulf of Alaska.
This image released by the NASA on the social media shows wind-blown plumes of dust skimming along the coast of the Gulf of Alaska, scientists believe these nutrient-bearing storms play a key role in fueling phytoplankton blooms.
Our satellites captured thick, wind-blown plumes of dust skimming along the coast of the Gulf of Alaska. Scientists believe these nutrient-bearing storms play a key role in fueling phytoplankton blooms. Take a look: https://t.co/W1TyUtIItf pic.twitter.com/QnXwAG4xYa
— NASA (@NASA) November 16, 2017

Leave a Comment